Sunglassman 的算法竞赛板子整理——图论篇
Sunglassman 的算法竞赛板子整理——图论篇
欧拉路径
P7771 【模板】欧拉路径
题目描述
求有向图字典序最小的欧拉路径。
输入格式
第一行两个整数 $n,m$ 表示有向图的点数和边数。
接下来 $m$ 行每行两个整数 $u,v$ 表示存在一条 $u\to v$ 的有向边。
输出格式
如果不存在欧拉路径,输出一行 No。
否则输出一行 $m+1$ 个数字,表示字典序最小的欧拉路径。
输入输出样例 #1
输入 #1
1 | 4 6 |
输出 #1
1 | 1 2 1 3 3 4 2 |
输入输出样例 #2
输入 #2
1 | 5 5 |
输出 #2
1 | 1 2 3 4 3 5 |
输入输出样例 #3
输入 #3
1 | 4 3 |
x #include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;constexpr int M = 2e5 + 10;namespace AC {int tr[M][26], fail[M], ed[M], sum[M], cnt = 0;vector adj[M];int insert(string ss) { int u = 0; for (char ch : ss) { int c = ch - ‘a’; if (!tr[u][c]) tr[u][c] = ++cnt; u = tr[u][c]; } return u;}void bfs() { queue q; for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i) { if (tr[0][i]) q.push(tr[0][i]); } while (!q.empty()) { int u = q.front(); q.pop(); for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i) { if (tr[u][i]) { fail[tr[u][i]] = tr[fail[u]][i]; q.push(tr[u][i]); } else { tr[u][i] = tr[fail[u]][i]; } } }}void dfs(int u) { for (auto v : adj[u]) { dfs(v); sum[u] += sum[v]; }}void work(vector& ss, string tar) { for (int i = 0; i < ss.size(); ++i) { ed[i] = insert(ss[i]); } bfs(); for (int i = 1; i <= cnt; ++i) { adj[fail[i]].push_back(i); } int u = 0; for (auto ch : tar) { int c = ch - ‘a’; u = tr[u][c]; sum[u]++; } dfs(0);}}int main() { int n; cin >> n; vector ss(n); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { cin >> ss[i]; } string tar; cin >> tar; AC::work(ss, tar); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { cout << AC::sum[AC::ed[i]] << ‘\n’; } return 0;}cpp
1 | No |
说明/提示
对于 $50%$ 的数据,$n,m\leq 10^3$。
对于 $100%$ 的数据,$1\leq u,v\leq n\leq 10^5$,$m\leq 2\times 10^5$。
保证将有向边视为无向边后图连通。
1 |
|
Dijkstra
P4779 【模板】单源最短路径(标准版)
题目描述
给定一个 $n$ 个点,$m$ 条有向边的带非负权图,请你计算从 $s$ 出发,到每个点的距离。
数据保证你能从 $s$ 出发到任意点。
输入格式
第一行为三个正整数 $n, m, s$。
第二行起 $m$ 行,每行三个非负整数 $u_i, v_i, w_i$,表示从 $u_i$ 到 $v_i$ 有一条权值为 $w_i$ 的有向边。
输出格式
输出一行 $n$ 个空格分隔的非负整数,表示 $s$ 到每个点的距离。
输入输出样例 #1
输入 #1
1 | 4 6 1 |
输出 #1
1 | 0 2 4 3 |
说明/提示
$1 \leq n \leq 10^5$;
$1 \leq m \leq 2\times 10^5$;
$s = 1$;
$1 \leq u_i, v_i\leq n$;
$0 \leq w_i \leq 10 ^ 9$,
$0 \leq \sum w_i \leq 10 ^ 9$。
1 | // Created by Sunglassman |
Kruskal求最小生成树
P3366 【模板】最小生成树
题目描述
如题,给出一个无向图,求出最小生成树,如果该图不连通,则输出 orz。
输入格式
第一行包含两个整数 $N,M$,表示该图共有 $N$ 个结点和 $M$ 条无向边。
接下来 $M$ 行每行包含三个整数 $X_i,Y_i,Z_i$,表示有一条长度为 $Z_i$ 的无向边连接结点 $X_i,Y_i$。
输出格式
如果该图连通,则输出一个整数表示最小生成树的各边的长度之和。如果该图不连通则输出 orz。
输入输出样例 #1
输入 #1
1 | 4 5 |
输出 #1
1 | 7 |
说明/提示
数据规模:
对于 $20%$ 的数据,$N\le 5$,$M\le 20$。
对于 $40%$ 的数据,$N\le 50$,$M\le 2500$。
对于 $70%$ 的数据,$N\le 500$,$M\le 10^4$。
对于 $100%$ 的数据:$1\le N\le 5000$,$1\le M\le 2\times 10^5$,$1\le Z_i \le 10^4$。
样例解释:
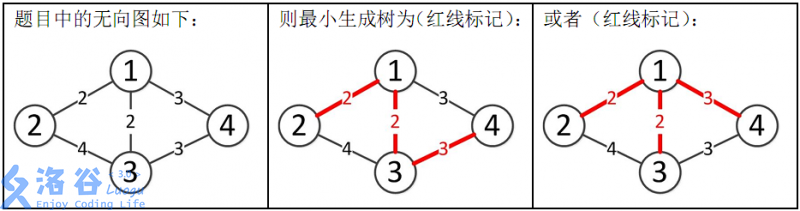
所以最小生成树的总边权为 $2+2+3=7$。
1 |
|
斜二进制LCA
1 |
|
Kruskal 重构树 & 倍增LCA
P1967 [NOIP 2013 提高组] 货车运输
题目背景
NOIP2013 提高组 D1T3
题目描述
A 国有 $n$ 座城市,编号从 $1$ 到 $n$,城市之间有 $m$ 条双向道路。每一条道路对车辆都有重量限制,简称限重。
现在有 $q$ 辆货车在运输货物, 司机们想知道每辆车在不超过车辆限重的情况下,最多能运多重的货物。
输入格式
第一行有两个用一个空格隔开的整数 $ n,m$,表示 A 国有 $ n$ 座城市和 $m$ 条道路。
接下来 $m$ 行每行三个整数 $x, y, z$,每两个整数之间用一个空格隔开,表示从 $x $ 号城市到 $ y $ 号城市有一条限重为 $z$ 的道路。
注意: $x \neq y$,两座城市之间可能有多条道路 。
接下来一行有一个整数 $q$,表示有 $q$ 辆货车需要运货。
接下来 $q$ 行,每行两个整数 $x,y$,之间用一个空格隔开,表示一辆货车需要从 $x$ 城市运输货物到 $y$ 城市,保证 $x \neq y$
输出格式
共有 $q$ 行,每行一个整数,表示对于每一辆货车,它的最大载重是多少。
如果货车不能到达目的地,输出 $-1$。
输入输出样例 #1
输入 #1
1 | 4 3 |
输出 #1
1 | 3 |
说明/提示
对于 $30%$ 的数据,$1 \le n < 1000$,$1 \le m < 10,000$,$1\le q< 1000$;
对于 $60%$ 的数据,$1 \le n < 1000$,$1 \le m < 5\times 10^4$,$1 \le q< 1000$;
对于 $100%$ 的数据,$1 \le n < 10^4$,$1 \le m < 5\times 10^4$,$1 \le q< 3\times 10^4 $,$0 \le z \le 10^5$。
1 |
|
Tarjan
TODO